Skin Glycation
Skin Glycation: How is Your Diet Aging You?
We all know that sugar is bad for us. It’s highly addictive, sneaking into our daily habits, and making it incredibly hard to quit. Did you know, that eating too much sugar ages you from the inside out? The sweet treats we love cause sugar molecules to attach to protein in your body, triggering a process that accelerates aging. Aging doesn’t start with fine lines and wrinkles – it begins at the cellular level, and it’s called Skin Glycation. This week, we are diving into skin health and wellness to help you turn back the clock and slow aging. Let’s get started!
What is Glycation?
Glycation is a natural, yet destructive process where sugars bind to proteins, forming harmful compounds, called, Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). In an article from PubMed, “The glycation process leads to a loss of protein function and impaired elasticity of tissues such as blood vessels, skin, and tendons. Because there are no enzymes to remove glycated products from the human body, the glycation process matches well with the theory that the accumulation of metabolic waste promotes aging.” Simply put, sugar breaks down amino acids – essential building blocks for our cells. Most don’t consume enough protein to restore our amino acids, resulting in premature aging. Glycation is also linked to serious diseases such as Diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and Cardiovascular Diseases.
What is Skin Glycation?
Skin glycation happens when sugars bind to proteins, creating Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) that damage our skin’s structure. According to PubMed, “Studies have shown that with the increase in the AGE content in the skin, volunteers developed skin problems such as yellowing, browning, poor elasticity, and deeper wrinkles.”
AGEs are divided into two categories:
⚫️ Endogenous AGEs: Naturally form and are part of the normal aging process. Over time, cells lose their function and we see visible signs of aging. PubMed defines Endogenous AGEs as, “Spontaneously formed and accumulate in the body under physiological metabolic conditions during normal aging, and the reaction process is slow due to the absence of enzymes.”
⚫️ Exogenous AGEs: Caused by inflammation, sugar, cigarettes, alcohol, and sun. PubMed defines Exogenous AGEs, “With the development of society and changes in the dietary habits of the population, the consumption of this highly processed food has increased exponentially, and AGEs may be the most important factor in the link between modern diet and health.”
Our poor lifestyles contribute to premature aging, yet we struggle to make the necessary changes. The good news is – you CAN slow glycation down!
What Causes Skin Glycation?
When AGEs form, they cause inflammation, the root cause of many skin and health issues. AGEs break down collagen and elastin – key proteins keeping our skin firm, youthful, and smooth. The result? More wrinkles, sagging, loss of elasticity, and rough textured skin. According to PubMed, “Several studies have indicated that AGEs accumulate after they are produced in the human body, which leads to the destruction of skin tissues by regulating gene expression, destroying protein structures, binding to RAGEs (receptors of AGEs), mediating a series of signaling pathways, and affecting the apoptosis and differentiation of skin-related cells. AGEs affect all levels of the skin, causing inflammation, aging, yellowing, and other issues.”
What Does Glycated Skin Look Like?
Glycated skin isn’t just about wrinkles and sagging skin – it has a distinct appearance. Here’s what to look for:
📌 Yellowing of the skin 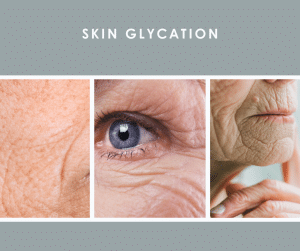
📌 Dull skin tone
📌 Cross-hatched wrinkles instead of fine lines
📌 Enlarged pores
📌 Rough textured skin
📌 Loss of firmness and elasticity
How Glycation Affects Skin Aging
Unlike traditional aging which appears as fine lines around the eyes, forehead, and mouth or sagging skin at the nasolabial folds, neck, and jawline – glycation has a more dramatic effect on the skin. PubMed defines, “The aging of the skin is first manifested as the aging of cells. Studies have shown that with aging, the proliferation and vitality of skin fibroblasts are reduced, leading to a decrease in the secretion of elastin fibers, collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and extracellular matrix in the dermis layer of the skin. This will result in a deepening and lengthening of skin wrinkles, pigmentation, and other manifestations of aging”. Glycation shows up as hatch-crossed wrinkles, textured skin around the mouth that appears as large pores, and loose skin with a wrinkle pattern instead of straight wrinkle lines.
How To Prevent Glycation
The key to preventing glycation is making smarter lifestyle choices. Here’s how you can slow down aging:
✅ Exercise regularly: Movement improves circulation and detoxes the body. A study published by PubMed found, “Life-long trained athletes had 21% lower contents of AGE cross-links in the patellar tendon compared to age-matched untrained subjects.”
✅ Limit alcohol intake: Alcohol is high in sugar and contributes to glycation. Alcohol has become a part of our culture despite many problems, including health and mental health problems. Alcohol disrupts gut health, leading to inflammation that affects our skin. A study from PubMed says, “During the metabolic process, alcohol produces acetaldehyde and generates reactive oxygen species, which affect the normal biological function of DNA through oxidative stress and epigenetic effects. This may result in damage to the immune system or even carcinogenesis.”
✅ Adopt a Skin-Friendly Diet: The foods we eat play a significant role in glycation. Sugary, processed, and fried, foods accelerate AGEs formation. Opt for proteins, less carbs, sugar, and fruits to support skin health. According to PubMed, “A wide variety of foods in modern diets are exposed to cooking or thermal processing for safety and convenience as well as to enhance flavor, color, and appearance. The fact that the modern diet is a large source of AGEs is now well-documented. Because it had previously been assumed that dietary AGEs (dAGEs) are poorly absorbed, their potential role in human health and disease was largely ignored.”
✅ Protect Your Skin From the Sun: Sun exposure worsens glycation. In an article by the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, “AGE accumulation is significantly increased in the dermis of photoaged skin and plays significant roles in photoaging. However, most AGEs are found to deposit in the dermis. This study showed that dermal AGEs could stimulate melanogenesis by activating NLRP3 inflammasome in human dermal fibroblasts.”
Protect your skin by:
✔️ Limit direct sun exposure during peak hours
✔️ Wear a zinc-oxide-based sunscreen
✔️ Wear a hat and protective clothing
Can You Reverse Skin Glycation?
Yes, and the key is to focus on healing your skin from the inside out. Here’s how:
📌 Take Vitamin D and Omega 3 supplements
📌 Increase protein intake, especially grass-fed red meats
📌 Limit alcohol consumption
📌 Exercise to keep the blood flowing and detox your body.
📌 Drink water to flush your system
📌 Prioritize skincare with anti-glycation ingredients
How To Treat the Skin
Skin treatments help reverse skin glycation when combined with a healthy lifestyle. Our recommendations are different than standard aging. Here are our Glycation Skin Treatment recommendations:
💎 BioRePeel combined with Red Light Therapy: Encourages cell renewal and collagen production
💎 Microneedling with Exosomes: Stimulates deep skin repair at the collagen level and reverses AGEs damage
💎 Microcurrent Treatments: Build muscle, strengthen collagen, and stimulate the lymphatic system for long-term maintenance
Ready to Restore Your Skin?
We are here to help guide you on your skin journey. If you’re ready to get started, please visit our website. Book the New Client Facial with us to kickstart your skin goals.
📆 Click here to get started and let us customize a treatment plan just for you
💬 Any questions, comment below – we are happy to help!




